The following are excerpts from www.sciencedirect.com

Leachate is defined as any contaminated liquid that is generated from water percolating through a solid waste disposal site, accumulating contaminants, and moving into subsurface areas. A second source of leachate arises from the high moisture content of certain disposed wastes. As these wastes are compacted or chemically react, bound water is released as “leachate.” In the absence of a confining barrier beneath or surrounding the waste disposal site, this leachate can migrate and contaminate subsurface and surface waters. The volume of leachate generated varies with the amount of precipitation and stormwater run-on and run-off, the volume of groundwater entering the waste-containing zone, and the moisture content and absorbent capacity of the waste material. When leachate is collected via perforated pipes, rainfall significantly affects leachate volume and contaminant concentrations.
Until now it is not possible to predict the leachate composition of a new landfill, and it is very difficult to describe the future leachate pollution of an existing landfill. As a consequence of the high organic waste content, uncontrolled anaerobic biological processes develop during the first up to 10years of landfill operation, which—with the influence of chemical/physical processes—determine the leachate quality particularly the organic carbon content of leachate. In addition, these processes influence the pH and the mobility of a variety of other compounds as iron, calcium, etc. Reducing the period of the anaerobic phase in a landfill results in a significant reduction of the leachate pollution. After the end of landfill operation, the leachate pollution will remain at high levels over a very long period of time (decades and longer) with only a slow decrease.
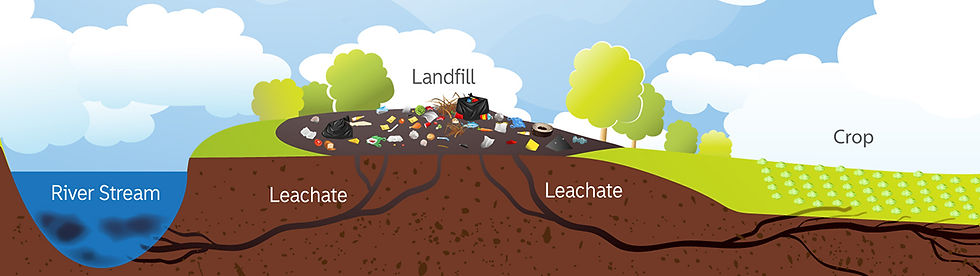
Leachate can penetrate the ground with time and contaminate the surface and groundwater resources. The real problem with leachate is that its chemical composition is hard to predict as it changes with the composition of the waste present. This requires the constant monitoring of the leachate produced. Also, the nearby soil and water bodies need to be monitored closely to avoid outbreak of any disease.

Leachates are hazardous and highly polluted wastewaters with considerable seasonal variations in chemical compositions and volumetric flow. Globally, the uptake of pollutants from leachates in the environment has resulted in environmental pollution particularly, surface and groundwater pollution and developmental disorders in humans such as congenital disabilities.
留言